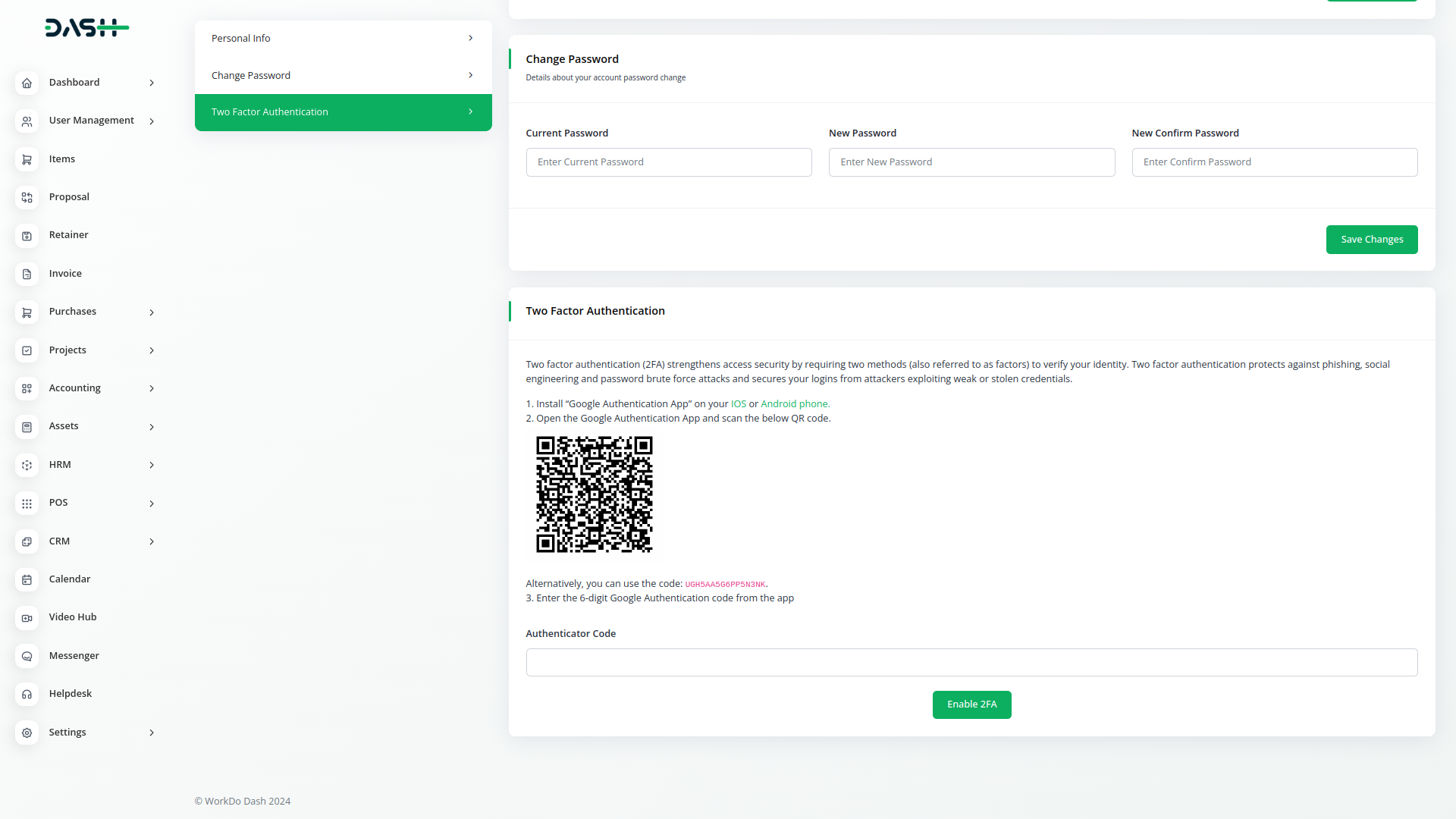
Google Authentication
Google Authenticator generates 2-Step Verification codes on your phone. 2-Step Verification provides stronger security for your Google Account by requiring a second verification step when you sign in. In addition to your password, youll also need a code generated by the Google Authenticator app on your phone.
Use Two-factor Authentication
Google Authenticator is a mobile security application based on two-factor authentication (2FA) that helps to verify user identities before granting them access to websites and services. Two-factor authentication makes it less likely that an intruder can masquerade as an authorized user.
Google Authenticator and how it works?
Google Authenticator is the application based on two-factor Authentication (2FA) that helps for identifying user identity and the confirmation on what a user claims to be and whether he actually is.
Google Authenticator is used for two-step verification based on Time-based One Time Password(TOTP) and HMAC-based One Time Password(HOTP) for authenticating users.
TOTP is an algorithm that computes a one-time password from a shared secret key and the current time. HTOP is an algorithm which uses hmac algorithm to generate one-time password.
Authenticator
Two-factor authentication makes it less likely that an intruder can masquerade as an authorized user. Authentication factors are categories of credentials used to verify that someone or something is who or what they are declared to be. There are three categories: Knowledge factors are credentials that the user knows, typically a user name and password; possession factors are things that the user has, typically a mobile phone; and inherence factors are things that the user is, typically a biometric characteristic such as a fingerprint or an iris pattern.
Why choose dedicated modulesfor Your Business?
With Dash, you can conveniently manage all your business functions from a single location.
Empower Your Workforce with DASH
Access over Premium Add-ons for Accounting, HR, Payments, Leads, Communication, Management, and more, all in one place!
- Pay-as-you-go
- Unlimited installation
- Secure cloud storage
Why choose dedicated modulesfor Your Business?
With Dash, you can conveniently manage all your business functions from a single location.